Introduction
This article shall describe a very simple approach to finding out information regarding the processes currently running on a machine. The demonstration application includes a collection of methods that may be used to search for specific processes using different criteria or to list out running processes.
Such information may be useful for a variety of reason, for example, if an application is dependent upon another application and that primary application must be up and running as a precursor to launching the dependent application, the methods contained in this demonstration will permit the code to test for the presence of the primary application prior to loading the dependent application. If, for example, an application were dependent upon a running copy of calc.exe, the code contained in the demonstration could be used to determine whether or not calc.exe was running prior to allowing the dependent application to run.
Alternatively, if an application launches other applications, the methods described herein could be used to determine whether or not that application successfully launched.
Everything contained in this demonstration is based upon the use of the Framework System.Management library. Aside from what is described in this demonstration, there are many other useful things that may be accomplished through the use of this library, for example one may start or kill processes using elements from System.Management.
This demonstration includes a class containing several methods used to either generate a list of applications or processes running on a machine, or to search for specific processes by means of different search criteria such as the application name, the process name, the process ID, or the process image name. The list related methods also provide information regarding other details about the process such as the memory size or caption bar title. What is demonstrated is only a small subset of the information available.

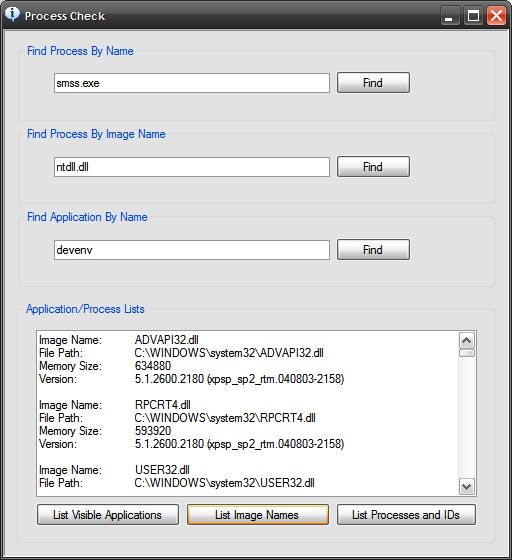
Figure 1: Getting a List of Running Applications.
Getting Started
The solution contains a single Windows Forms project called ApplicationCheck.vb which was written in VISUAL BASIC 2005; the application contains a form (Form1.vb) and a class (ProcessValidation.vb).

Figure 2: Solution Explorer with the Project Visible
Code: ProcessValidation (ProcessValidation.vb)
All of the code used to list processes or search for running processes is contained in the ProcessValidation class.
The code for this class begins with the following:
Imports System.Text
Imports System.Management
Public Class ProcessValidation
Note that the System.Management library has been added to the imports for this class. Following the imports, the declaration of the class, the remainder of the class is used to provide the methods used to list process information or to search for the presence of a current process.
The class and all contained methods were declared as shared and are therefore immediately available to the application.
The first method available in the class is the ListAllProcesses method. This method creates an instance of the Management Class, passing in the argument Win32_Process. This is then used to populate a Management object with a collection of all instances of the class. The list is then built by iterating through the collection and adding the process name and ID to the stringbuilder. The method returns the string to the calling method which is, in this case used to print the list of processes and IDs to a textbox contained in the demonstration application. Note that you can pass other optional arguments to the Management class aside from Win32_Process; for example, to get a list of services, you can pass in the argument Win32_Services.
Public Shared Function ListAllProcesses() As String
Dim sb As New StringBuilder()
Dim MgmtClass As New ManagementClass("Win32_Process")
Dim mo As New ManagementObject()
For Each mo In MgmtClass.GetInstances
sb.Append("Name: " & mo("Name") & Environment.NewLine)
sb.Append("ID: " & mo("ProcessId") & Environment.NewLine)
sb.Append(Environment.NewLine)
Next
Return sb.ToString()
End Function
Using a slightly different approach, the next method lists all running applications by first getting a list of all local processes and then checking to see if the process has a visible Main Window Title (by checking to see if the caption bar contains text). If the process contains a window with a caption showing some text, this method will regard it as an open and visible application and will then list out the title, process name, window handle, and memory allocation for that particular process.
Public Shared Function ListAllApplications() As String
Dim sb As New StringBuilder()
Dim p As New Process()
For Each p In Process.GetProcesses(".")
Try
If p.MainWindowTitle.Length > 0 Then
sb.Append("Window Title: " +
p.MainWindowTitle.ToString() + Environment.NewLine)
sb.Append("Process Name: " + p.ProcessName.ToString() +
Environment.NewLine)
sb.Append("Window Handle: " +
p.MainWindowHandle.ToString() + Environment.NewLine)
sb.Append("Memory Allocation: " +
p.PrivateMemorySize64.ToString() + Environment.NewLine)
sb.Append(Environment.NewLine)
End If
Catch
End Try
next
Return sb.ToString()
End Function
The next method is used to list all processes by image name. This method works in a manner consistent with the previous example but obtains the module information associated with the process and then returns a string containing module level information to include the image name, file path, memory size, and software version.
Public Shared Function ListAllByImageName() As String
Dim sb As New StringBuilder()
Dim p As New Process()
For Each p In Process.GetProcesses(".")
Try
Dim pm As ProcessModule
For Each pm In p.Modules
sb.Append("Image Name: " + pm.ModuleName.ToString() +
Environment.NewLine)
sb.Append("File Path: " + pm.FileName.ToString() +
Environment.NewLine)
sb.Append("Memory Size: " +
pm.ModuleMemorySize.ToString() + Environment.NewLine)
sb.Append("Version: " +
pm.FileVersionInfo.FileVersion.ToString() +
Environment.NewLine)
sb.Append(Environment.NewLine)
Next
Catch
End Try
Next
Return sb.ToString()
End Function
The next method is used to search for a running instance of a process on the local machine by process name. If the method is able to locate the process, it will return true; if the process is not found, the method will return false.
Public Shared Function CheckForProcessByName_
(ByVal processName As String) As Boolean
Dim MgmtClass As New ManagementClass("Win32_Process")
Dim rtnVal As Boolean = False
Dim mo As New ManagementObject()
For Each mo In MgmtClass.GetInstances()
If mo("Name").ToString().ToLower() = processName.ToLower() Then
rtnVal = True
End If
Next
Return rtnVal
End Function
The next method is used to search for a running instance of a process on the local machine by image name. If the method is able to locate the process, it will return true; if the process is not found, the method will return false.
Public Shared Function CheckForProcessByImageName_
(ByVal processImageName As String) As Boolean
Dim rtnVal As Boolean = False
Dim p As New Process()
For Each p In Process.GetProcesses(".")
Dim pm As ProcessModule
Try
For Each pm In p.Modules
If pm.ModuleName.ToLower() = processImageName.ToLower() Then
rtnVal = True
End If
Next
Catch
End Try
Next
Return rtnVal
End Function
The next method is used to search for a running instance of a process on the local machine by application name. If the method is able to locate the process, it will return true; if the process is not found, the method will return false.
Public Shared Function CheckForApplicationByName_
(ByVal AppName As String) As Boolean
Dim rtnVal As Boolean = False
Dim p As New Process()
For Each p In Process.GetProcesses(".")
Try
If p.ProcessName.ToLower() = AppName.ToLower() Then
rtnVal = True
End If
Catch
End Try
Next
Return rtnVal
End Function
Code: Main Form (Form1.vb)
This Form class is used to demonstrate the use of the methods exposed in the ProcessValidation.vb class. The Form class is pretty simple and the annotation describes the purpose of each part of the class.
Public Class Form1
Private Sub btnListAll_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnListAll.Click
txtAllProcesses.Text = String.Empty
txtAllProcesses.Text = ProcessValidation.ListAllProcesses()
End Sub
Private Sub btnListAllApps_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnListAllApps.Click
txtAllProcesses.Text = String.Empty
txtAllProcesses.Text = ProcessValidation.ListAllApplications()
End Sub
Private Sub btnListImages_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnListImages.Click
txtAllProcesses.Text = String.Empty
txtAllProcesses.Text = ProcessValidation.ListAllByImageName()
End Sub
Private Sub btnSearch_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnSearch.Click
Dim bTest As Boolean = _
ProcessValidation.CheckForProcessByName(txtSearchProcess.Text.ToString())
Select Case (bTest)
Case True
MessageBox.Show(txtSearchProcess.Text + " process name found.")
Case False
MessageBox.Show(txtSearchProcess.Text + " process name not found.")
Case Else
End Select
End Sub
Private Sub btnSearchImgname_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnSearchImgname.Click
Dim bTest As Boolean = _
ProcessValidation.CheckForProcessByImageName(txtImageName.Text.ToString())
Select Case (bTest)
Case True
MessageBox.Show(txtImageName.Text + " process name found.")
Case False
MessageBox.Show(txtImageName.Text + " process name not found.")
Case Else
End Select
End Sub
Private Sub btnFindApp_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnFindApp.Click
Dim bTest As Boolean = ProcessValidation.CheckForApplicationByName_
(txtApplicationName.Text.ToString())
Select Case (bTest)
Case True
MessageBox.Show(txtApplicationName.Text + " process name found.")
Case False
MessageBox.Show(txtApplicationName.Text + " process name not found.")
Case Else
End Select
End Sub
End Class
Summary
This article was intended to demonstrate a simple approach to obtain information about the processes running on a machine. The methods contained in the demonstration application show several approaches for how to list out information regarding running processes as well as how to search for a specific process.
This member has not yet provided a Biography. Assume it's interesting and varied, and probably something to do with programming.
 General
General  News
News  Suggestion
Suggestion  Question
Question  Bug
Bug  Answer
Answer  Joke
Joke  Praise
Praise  Rant
Rant  Admin
Admin