Introduction
This brief article describes how to transform an NMEA-string (i.e. from a
a GPS-device) to the Swedish National Grid (RT90).
I will not go through the SerialPort communication or NMEA interpretation issues
as they are well described by Jon Person in:
- Writing Your Own GPS Applications: Part 1.
- Writing Your Own GPS Applications: Part 2.
and by Alex@UEA:
- GPS- Deriving British Ordnance Survey Grid Reference from NMEA data
Background
As I was writing my Physics application at work (which included communicating with a GPS-device) I came across the articles listed above.
The NMEA-Interpreter-article by Jon Person was especially helpful (thanks Jon), but naturally none of them covered how to transform
the NMEA-string (based upon the WGS 84 Ellipsoid) to the Swedish National Grid (Rikets Koordinatsystem 1990 or just RT90) which
seems to be used by most maps in Sweden. I also found a lot of helpful information at Lantmäteriet,
where projection/transform formulas were provided. All that was needed was to implement the transform, preferably in C#. So here it is.
Using the code
The code is simply a single class which reads NMEA strings, such as those given by Jon Person's NMEA-Interpreter, and transforms
them into RT90 Cartesian coordinates (x, y). I also included support for 6 different regions in Sweden, ranging from Luleå in the East to
Göteborg in the West, as recommended by Lantmäteriet. The regions are called 5 gon O, 2.5 gon O, 0 gon V, 2.5 gon V, 5 gon V and 7.5 gon V.
Major (in a Swedish sense) cities are from East to West: Luleå, Umeå, Stockholm, Örebro, Malmö and Göteborg.
(Note:The 'V' and 'O' is used instead of 'W' and 'E' since the Swedish words for west/east starts with a 'V'/'O'...)
The Class is called GaussKrugerProjection as it is the conformal projection method in use, i.e.
a "Projection which preserves the original shape of the area of interest but not the area or distance".
It is simply used as follows:
GaussKrugerProjection myTransformInStockholm = new GaussKrugerProjection("0V");
or if you're around Göteborg (Gothenburg):
GaussKrugerProjection myTransformInGothenburg = new
GaussKrugerProjection("7.5V");
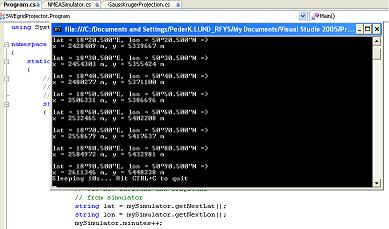
If we have received an NMEA string from, for example, the NMEA-Interpreter mentioned above, we just send it to the projection
using the GetRT90 method in the GaussKrugerProjection class:
public int[] GetRT90(string lat, string lon)
...using the created projection instance above and assuming we have a NMEAInterpreter:
private void NMEAInterpreter_PositionReceived(string lat, string lon)
{
int[] XandY = myTransformInStockholm.GetRT90(lat, lon);
int x = XandY[0];
int y = XandY[1];
Console.WriteLine("x = {0}, y = {1}", x.ToString(), y.ToString());
}
The Class is written for NMEA-strings in the format
string lat = "20°18.2274\"E";
Where 20 is hours, 18 minutes, 22.74 seconds and E represents the Hemisphere.
Make sure your NMEA string is formatted in the same way.
The GaussKrugerProjection class is basically divided into two parts:
- A NMEA-string to radians Parser (smilar to that in article (3) above)
- A Projection Calculator.
The parser looks like this:
private double GetLatLong(string LatorLong, bool isLong)
{
double deciLatLon = Convert.ToDouble(
LatorLong.Substring(0, LatorLong.IndexOf("°"))
);
LatorLong = LatorLong.Substring(LatorLong.IndexOf("°") + 1);
deciLatLon +=
(Convert.ToDouble(LatorLong.Substring(
0, LatorLong.IndexOf(".")), enUSCultureInfo)
) / 60.0;
LatorLong = LatorLong.Substring(LatorLong.IndexOf(".") + 1);
string sec = LatorLong.Substring(0, LatorLong.IndexOf("\""));
deciLatLon +=
(
Convert.ToDouble(sec.Insert(2, "."), enUSCultureInfo)
) / 3600.0;
LatorLong = LatorLong.Substring(
LatorLong.IndexOf("\"") + 1);
if (isLong && LatorLong == "S" ||
!isLong && LatorLong == "W")
{
deciLatLon = -deciLatLon;
}
return deciLatLon * (Math.PI / 180.0);
}
The projection calculator can be divided into two parts:
- Declaring variables / pre-projection calculation and
- Performing projection.
First thing's first: here are the variable declarations:
#region Fields
private static double a = 6378137.0;
private static double f = (1.0 / 298.2572221010);
private static string CM_0V = "18°03.2268\"E";
private static double k0_0V = 1.000005400000;
private static double FN_0V = -668.844;
private static double FE_0V = 1500083.521;
private string CM;
private double k0;
private double FN;
private double FE;
private double lat;
private double lon;
private double A, B, C, D, Beta1, Beta2, Beta3, Beta4,
e2, n, aHat;
private double x;
private double y;
private static CultureInfo enUSCultureInfo =
new CultureInfo("en-US");
#endregion
There exists similar Fields for all 6 different gons. These are then used by the Constructor as:
public GaussKrugerProjection()
{
CM = CM_25V;
k0 = k0_25V;
FN = FN_25V;
FE = FE_25V;
this.Initialize();
}
private void Initialize()
{
e2 = f * (2.0 - f);
n = f / (2.0 - f);
aHat = (a / (1.0 + n)) * (1.0 +
(0.25 * Math.Pow(n, 2)) +
((1.0 / 64.0) * Math.Pow(n, 4)));
A = e2;
B = (1.0 / 6.0) * (5.0 * Math.Pow(A, 2) -
6.0 * Math.Pow(A, 3));
C = (1.0 / 120.0) * (104.0 * Math.Pow(A, 3) -
45.0 * Math.Pow(A, 4));
D = (1.0 / 1260.0) * (1237.0 * Math.Pow(A, 4));
Beta1 = (0.5 * n) - ((2.0 / 3.0) * Math.Pow(n, 2)) +
((5.0 / 16.0) * Math.Pow(n, 3)) +
((41.0 / 180.0) * Math.Pow(n, 4));
Beta2 = ((13.0 / 48.0) * Math.Pow(n, 2)) -
((3.0 / 5.0) * Math.Pow(n, 3)) +
((557.0 / 1440.0) * Math.Pow(n, 4));
Beta3 = ((61.0 / 240.0) * Math.Pow(n, 3)) -
((103.0 / 140.0) * Math.Pow(n, 4));
Beta4 = ((49561.0 / 161280.0) * Math.Pow(n, 4));
}
And finally the actual projection:
private void CalcGaussKrugerProjection(double lat, double lon)
{
double phiStar = lat - (Math.Sin(lat) * Math.Cos(lat) * (
A +
B * Math.Pow(Math.Sin(lat), 2) +
C * Math.Pow(Math.Sin(lat), 4) +
D * Math.Pow(Math.Sin(lat), 6)));
double dLon = lon - GetLatLong(CM, true);
double chi = Math.Atan(Math.Tan(phiStar) / Math.Cos(dLon));
double z = Math.Cos(phiStar) * Math.Sin(dLon);
double eta = 0.5 * Math.Log((1.0 + z) / (1.0 - z));
x = k0 * aHat * (chi +
Beta1 * Math.Sin(2.0 * chi) * Math.Cosh(2.0 * eta) +
Beta2 * Math.Sin(4.0 * chi) * Math.Cosh(4.0 * eta) +
Beta3 * Math.Sin(6.0 * chi) * Math.Cosh(6.0 * eta) +
Beta4 * Math.Sin(8.0 * chi) * Math.Cosh(8.0 * eta)) +
FN;
y = k0 * aHat * (eta +
Beta1 * Math.Cos(2.0 * chi) * Math.Sinh(2.0 * eta) +
Beta2 * Math.Cos(4.0 * chi) * Math.Sinh(4.0 * eta) +
Beta3 * Math.Cos(6.0 * chi) * Math.Sinh(6.0 * eta) +
Beta4 * Math.Cos(8.0 * chi) * Math.Sinh(8.0 * eta)) +
FE;
}
If you're interested in the Mathematical details, see:
this page or
this PDF for more information (the first is in Swedish).
History
This is the first version.
- Cheers!
Peder has a background in engineering physics and is currently PhD student in medical radiation physics at Lund University.
 General
General  News
News  Suggestion
Suggestion  Question
Question  Bug
Bug  Answer
Answer  Joke
Joke  Praise
Praise  Rant
Rant  Admin
Admin