Introduction
Large enterprise solutions may have different parts and each part may need different development/deployment environment. For example, a project may have a part to work with third party web service. Now not all developers are interested for codes works with that web service. For faster/smooth development, developers who are not working with that web service may not want to interact with the service. Every time a developer runs/debugs the code and if the web service is invoked (which may kill time), then it’ll be annoying for developers who don’t work with that part of the code. So how can we fix this problem where people who are working with web service will invoke web service whereas people who are not working with web service will not invoke web service?
1. Create a New Configuration
In Visual Studio (VS), you can create custom configuration beyond DEBUG and RELEASE. Right click on the Solution in VS and click Configuration. In this configuration window, select ‘New’ in the dropdown under ‘Active Solution Configuration:’. You’ll be prompted with the following window.
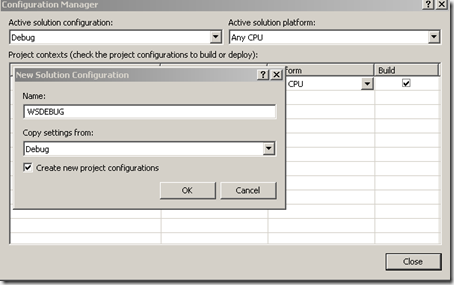
Figure 1: Create Custom Configuration from Configuration Manager.
Now enter a meaningful name for the configuration and select the base configuration (DEBUG or RELEASE).
2. Create Conditional Compilation Symbol for the Configuration
Make sure that the new configuration is selected for the solution. To make sure of this, open ‘Configuration Manager’ by right clicking on the solution. The following figure shows that the custom configuration is selected for the solution.

Figure 2: Select Custom Configuration from Configuration Manager
Now open the properties window of the project you want to work differently for this configuration. Select Build tab and enter a conditional symbol name (WSDEBUG_SYMBOL in the figure) as shown below:

Figure 3: Create a conditional symbol for custom configuration
FYI, here the conditional compilation symbol will be associated with configuration name. So this conditional symbol will be active only when you select that particular configuration under which the symbol created.
3. Use Conditional Compilation Symbol in Code
Since conditional compilation symbol is associated with configuration name, whenever you’ll select any configuration any project/solution, any symbols defined in that project/solution will be active. Now code block which needs to be conditional compiled can be put in a condition below:
#if WSDEBUG_SYMBOL
Console.WriteLine("This is WSDEBUG");
#else
Console.WriteLine("This is not WSDEBUG");
#endif
In the above code block, if you select any configuration that has any conditional compilation symbol named “WSDEBUG_SYMBOL” defined, then the first condition will be executed either else condition will be executed. Now, you can write your code inside custom compilation section. So all you need to do is to change your configuration from DEBUG to your custom one (as like WSDEBUG).
Conclusion
One nice thing about VS is that it doesn’t keep track of the project’s configuration, user selected for a project/solution, inside project or solution. Rather, it keeps this information in a file named like “yourproject.csproj.FileListAbsolute.txt”. So as long as you don’t keep this file in source control, different user’s configuration for project/solution will be kept locally. So if developer dev1 changes project or solution’s configuration to WSDEBUG, then no other developer’s local settings will be affected.
So the solution is now that if you need different settings than others, then create your own configuration and conditional compilation symbol. Then use that symbol for conditional compiling. Since your project/solution preference is kept locally, every time you’ll open the solution, you’ll find your custom configuration selected whereas other developers will be using their own configurations. So the final answer to the question I had asked at the top of the post is “developers who wants to work with web service may select their custom configuration to use whereas developers who don’t want to work with web service may use default DEBUG configuration”
codeproject
Sohel has more than six years of experience in professional software development with extensive involvement in Web based Object-Oriented, Multi-Tiered application design and development. He's Familiar with Test Driven Development (TDD) and refactoring techniques as well as having expertise in architecturing large enterprise applications. He has Experience in working with Content Management System and Portal Management System tools like SharePoint, DotNetNuke, Ektron.
Over last few years, he’s involved in development with projects on Microsoft SharePoint and received Microsoft MVP for SharePoint Server Development in the year 2011 and 2012. Currently he's working in a software company located Copenhagen,Denmark on a project integrating SharePoint and SAP. You can read his popular blog at: http://ranaictiu-technicalblog.blogspot.com
 General
General  News
News  Suggestion
Suggestion  Question
Question  Bug
Bug  Answer
Answer  Joke
Joke  Praise
Praise  Rant
Rant  Admin
Admin