Things to be taken care by developers while writing code or designing different layers
Presentation Layer:
- Choose your UI elements carefully
- Optimize Viewstate
- State management should be effective and optimized well
- Well Managed Caching
- Reduce round trips to server
- Utilize client side script effectively
- Consider Asynchronous calls
- Consider Partial / Ajax calls to make the portion of the page update
- Consider pagination for large record sets and provide server side pagination if possible
Choose UI Elements Carefully
The control selection is one important part in ASP.NET web page performance. As you know the Page Life Cycle and Server Control Life Cycle it has to load after executing few events which will take some more extra time for control processing and rendering. So choose your controls wisely.
First we should discuss about data controls, these are most used controls in any web application to show data sets or records.
There are majorly four data controls in asp.net those are
- DataList
- GridView
- ListView and
- Repeater
Who have these controls to show data records in their own passion. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages according to features. When we consider performance the order of these controls would be Repeater, ListView, DataList, and GridView
Repeater:
Repeater control is derived from Control class. Repeater simply repeats data given in templates. Repeated data is usually HTML code mixed with records from data source. Repeater's output is not predefined. Because of that, Repeater demands most work to define template. In return it gives us most flexibility to build layout and optimize presentation.
With same template and same data set, Repeater usually works faster of DataList or GridView controls. This is mostly because of DataReader class, which is used for read only access. DataReader is faster than DataSet or DataTable classes commonly used with GridView.
Compared to GridView and DataList control, Repeater has limited features. By default, Repeater is good for displaying of data. It is not best choice if you need editing of data. Also, by default it doesn't provide paging and sorting of records.
ListView:
ListView control is newest data presentation control, introduced in ASP.NET 3.5. Previous controls (Repeater, DataList and GridView) logically follow each other. For example, Repater is simplest but fastest, then DataList has more features but more overheads too, and finally GridView is most complex, has most features, but heaviest and thus slowest on page.
Now, there is new ListView control which tries to provide best from both sides: speed and flexibility in design, and also a lot of features like paging, updating or deleting of records etc. Because of this, ListView control is often better choice than Repeater or DataList.
Flexibility in design comes with price. To use ListView, you'll probably have to write a lot of markup code. For simple table layout, GridView requires much less work.
ListView has new LayoutTemplate. Instead of Header and Footer templates, ListView has just LayoutTemplate. Main advantage of LayoutTemplate when compared to Header and Footer templates is that LayoutTemplate makes markup code looks more object oriented. So, it is not a big difference between these two models. It is possible to achieve same results with LayoutTemplate on ListView like with HeaderTemplate and FooterTemplate on Repeater, DataList and GridView.
DataList:
Unlike Repeater, DataList control is derived from WebControl class. That gives it a number of style properties like BorderStyle, BackColor, ForeColor etc.
DataList is somewhere between Repeater and GridView, in many ways looks like a compromise between these two. DataList has more features but more limited in design when compared to Repeater. In the other hand, it has more flexibility and less features than GridView.
Also, DataList has RepeatDirection, RepeatColumns and RepeatLayout properties, which are unique for DataList control. These properties are useful when you need to create presentation with more than one record per row, like image gallery, product catalog etc. For example, let say you are creating an image gallery and want to show 5 images per row. Repeater would require checking of record position and manipulating HTML. With DataList, just use RepeatDirection="Horizontal" and RepeatColumns="5". RepeatLayout could be Table or Flow, depending of do you need HTML table structure in layout.
GridView:
Like DataList control, GridView is derived from WebControl class and includes numerous style properties. In addition to this, GridView is most complex control and have most properties. Numerous features include data paging, sorting, updating and deleting of records. First versions of ASP.NET had DataGrid control. GridView is replaced DataGrid in ASP.NET 2.0 as improved version of old DataGrid control.
GridView displays data in form of grid. Rows and columns are represented as HTML table. This is very useful if you need grid-like presentation. If you need to present data in table layout, then GridView requires a minimum of effort. In same time, if you want more customizable flow layout, GridView is not best option.
Common problem when using GridView control could be large ViewState which makes page loads slower and requires more bandwidth. This could be insignificantly on low traffic website, but keep in mind that for each second while the page loads, the percentage of visitors will become impatient and leave website. Also, massive view state is not good for SEO (search engine optimization).
One more problem is using of default pager on large tables or high traffic websites. If default paging is used, GridView will load complete dataset in memory, which descreases website's performances.
HTML Elements VS ASP.NET Server Controls
When compared both the controls HTML are pretty fast. On other hand the server controls are slow because of their rendering process. all server controls when the actual page loads they will render as normal html elements. ASP.NET rendering engine has to render the server controls equivalent html text according to the browser to where the content should render. This is an extra process when compared with normal HTML elements.
The benefits of server controls are very high when compared with normal HTML elements
- They have state, so on each page post back we can preserve the value of the control and will be bind after post back.
- They are object oriented so we can handle the public properties of the controls from code behind.
- They provide caching feature so that we can preserve the value across page navigation
- We can attach server events to server controls where we can not attach them to html controls directly.
ViewState Optmization
ViewState is hidden field, which holds all other controls values in BASE64 format and resides on same page. The scope of ViewState is limited to the page. All server controls in a asp.net page maintain their state by means of ViewState.
The ViewState process is very simple. Whenever page postback occurs all the server control values and their state will be saved in ViewState. Once the postback is over the respective values will be binded to controls. To understand this cycle refer Page Life Cycle. The below figure explains how what are the values saved in ViewState with respect each server control
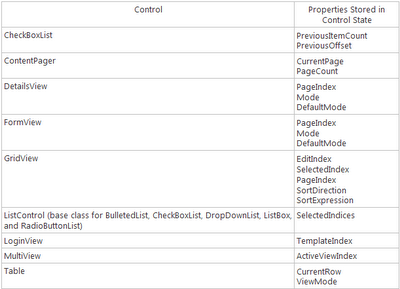
For more information on ViewState Optimization please click Here
The ASP.NET Wiki was started by Scott Hanselman in February of 2008. The idea is that folks spend a lot of time trolling the blogs, googlinglive-searching for answers to common "How To" questions. There's piles of fantastic community-created and MSFT-created content out there, but if it's not found by a search engine and the right combination of keywords, it's often lost.
The ASP.NET Wiki articles moved to CodeProject in October 2013 and will live on, loved, protected and updated by the community.
