Exception Message Box Using C#
4.47/5 (77 votes)
Allows applications to display detailed and formatted error messages
Introduction
Exceptions are unavoidable factors in development. Here I explain how to display the exception occurred in a detailed and in the best formatted way.
This displays a message box that can be customized with text, buttons, and symbols to improve the customer experience with a Microsoft Windows .NET Framework.
ApplicationExceptionMessagebox helps any developer to display an error message in the best formatted way. The user is given a choice to add up user defined messages as shown in DetailErrorMessage.jpg. ExceptionMessageBox gives the user an option whether to display the same message again and again in the application. Like the usual MessageBox in C#, we have an option to display a button as per the need. In the above example, I have used only Yes and No buttons.
Background
The user is requested to add a .NET reference named ExceptionMessageBox and a namespace using Microsoft.SqlServer.MessageBox;
Using the Code
I have created a solution named ExceptionMessageBoxSample. First I added a Windows Form named Form1.cs to my solution. On the form load, I am implicitly throwing an exception which will be caught by my catch block.
STEP 1: Add the .NET Reference ExceptionMessagebox and add the namespace in the code:
//
//using Microsoft.SqlServer.MessageBox;
//
STEP 2: The try-block contains the guarded code block that may cause the exception. The block is executed until an exception is thrown or it is completed successfully. Here I am implicitly throwing an exception.
try
{
// Do something that you don't expect to generate an exception.
throw new ApplicationException
("An unexpected error occurred. Please call Helpdesk.");
}
STEP 3: The catch clause can be used without arguments, in which case it catches any type of exception, and is referred to as the general catch clause. It can also take an object argument derived from System.Exception, in which case it handles a specific exception.
catch (ApplicationException ex)
{
// Define a new top-level error message.
string str = "Write the reason why the action failed.";
// Add the new top-level message to the handled exception.
ApplicationException exTop = new ApplicationException(str, ex);
exTop.Source = this.Text;
// Information in the Data property of an exception that has a name
// beginning with "HelpLink.Advanced" is shown when the user
// clicks the Advanced Information button of the exception message
// box dialog box.
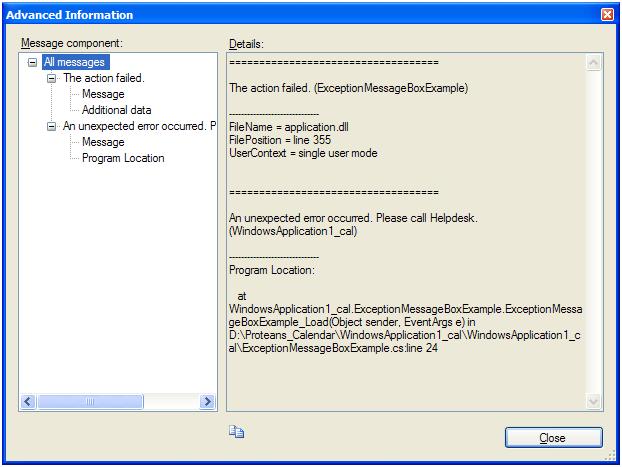
exTop.Data.Add("AdvancedInformation.FileName",
"ExceptionMessageBoxSample.dll");
exTop.Data.Add("AdvancedInformation.FilePosition", "line 24");
exTop.Data.Add("AdvancedInformation.UserContext",
"a detail message can be given");
// Show the exception message box with additional information that
// is helpful when a user calls technical support.
ExceptionMessageBox box = new ExceptionMessageBox(exTop);
box.Buttons = ExceptionMessageBoxButtons.YesNo;
box.Caption = "Caption";
box.ShowCheckBox = true;
box.ShowToolBar = true;
box.Symbol = ExceptionMessageBoxSymbol.Stop;
box.Show(this);
}
Add the new top-level message to the handled exception ApplicationException. The string variable str is used to display the ApplicationException source.
Now we are all done. Now you can execute the program and see the result.
Points of Interest
ExceptionMessage box does have pre-defined properties. Some of them are:
Beep: Specifies whether to play an audible sound when the message is displayedData: Gets theIDictionaryinterface that stores help link and advanced information associated with the top-level messageOption: Gets or sets miscellaneous display options for the message boxShowCheckBox: Specifies whether to show the check box in the exception message box
History
- 18th May, 2007: First release
This is my first article on The Code Project. I will be modifying the document later on.
About Shiras
Currently I am working as a Senior Software Engineer at Proteans Software Solutions in Bangalore.
