Introduction
This article shows you a useful technique to cache some of that page data on the browser in-memory. Since we use Ajax, the page is not reloaded each time. This prevents the cache from being invalidated on each round-trip. Client-side caching is sometimes required for performance reasons and also to take the load off of the DBMS. Since most modern PCs have plenty of RAM to spare, client-side caching becomes an important weapon in the modern programmer's arsenal of tricks.
With the advent of Ajax, application data can be maintained on the client without the use of ViewStates (aka hidden fields) or to a lesser degree, cookies. As any experienced developer will tell you, ViewState is a double-edged sword. Indiscriminate use of ViewStates can really have a detrimental effect on performance - what with the Viewstate payload ferried to and from the server with every postback.
 This begs the question: Can we use this technique without Ajax? AFAIK, the answer is: "No." That is so because we are maintaining the cache as a page-level variable on the client. The moment the page is refreshed via a full-page postback, the cache is invalidated. Keep this in mind while designing your application.
This begs the question: Can we use this technique without Ajax? AFAIK, the answer is: "No." That is so because we are maintaining the cache as a page-level variable on the client. The moment the page is refreshed via a full-page postback, the cache is invalidated. Keep this in mind while designing your application.
The accompanying code can be extended to use record data too, via JavaScript and the presentation logic can also be hived off to a JavaScript routine on the client. We could even pipe XML down to the client and it could be parsed and presented through client-side script.
To keep this sample code easy to comprehend, I have rendered the tabular data from within the Web Service itself - which may not be architecturally optimal. Since this is not a treatise on design best-practices, I have taken the liberty of cutting corners here and there for the sake of brevity.
 We use JavaScript associative arrays to maintain our client-side cache. One thing to be noted about JS associative arrays is that once you associate a
We use JavaScript associative arrays to maintain our client-side cache. One thing to be noted about JS associative arrays is that once you associate a string key with an array, there is no way to iterate through the array using indexes. Supposing you are using it like this: asarray["akey"] = <value> there is no way you can revert to accessing the elements by their ordinal position like this: var anyvar = asarray[0].
Using the Code
Let us examine the critical sections of the code that are absolutely necessary for client-side caching to work. The rest of the code deals with presentation and layout and a discussion on these aspects will be skipped.
For those who subscribe to the view that source-code is the ultimate documentation, you may skip this section. For the others, we'll try to separate the wheat from the chaff. Let us look at the most important pieces of code that makes client-side caching with Ajax and Javascript possible. I am using XML data for demonstration purposes and this makes the project run without having to change connection strings or even having SQL Server installed on your computer.
Step 1
Create a New Website and choose "ASP.NET AJAX-Enabled Website". If you do not have .NET 2.0 Ajax Toolkit installed, go here and download them. You cannot begin this exercise without it.
Step 2
Select "Add New Item" by right-clicking on the project in Solution Explorer and choose "Web Service". Add the highlighted code to your web service class. The [ScriptService] attribute decoration makes the web service class callable by the Ajax framework. You have to include using System.Web.Script.Services to be able to do that.
IMPORTANT: You must have installed Microsoft ASP.NET Ajax 1.0 and the Ajax Toolkit for this sample to work. Add a reference to AjaxControlToolkit.dll (not included in the distribution) for the code sample to work You will find it here.
using System.Web.Script.Services;
...
[ScriptService]
public class DataAccess : System.Web.Services.WebService
{ ...
Step 3
Flesh out your web method to do something useful. Our example does this:
[WebMethod]
public string FetchOrders(string key)
{
return LoadData(key);;
}
private string LoadData(string key)
{
DataSet ds = new DataSet();
ds.ReadXml(this.Context.Server.MapPath("App_Data\\northwind.xml"));
ds.Tables["Orders"].DefaultView.RowFilter = "customerid = '" + key + "'";
return RenderResultTable((ds.Tables["Orders"].DefaultView));
}
private string RenderResultTable(DataView rdr)
{
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
str.AppendLine("<table cellspacing=\"0\" cellborder=\"=0\"
cellpadding=\"5\">");
str.AppendLine("<tr><td><b>Order Date</b></td><td><b>Order ID</b>
</td></tr>");
foreach(DataRowView drv in rdr)
{
str.AppendLine("<tr>");
str.AppendFormat("<td>{0}</td> <td>{1}</td>", drv["OrderDate"],
drv["OrderID"]);
str.AppendLine("</tr>");
}
str.AppendLine("</table>");
return str.ToString();
}
Step 4
Now, we go to the client script that does the actual caching and retrieves data by making a call to the web service. This employs rudimentary JavaScript - no surprises here.
var cacheData = new Array();
var currSel = null;
var seedData = "0BFA4D6B-DD18-48aa-A926-B9FD80BFA5B7";
Step 5
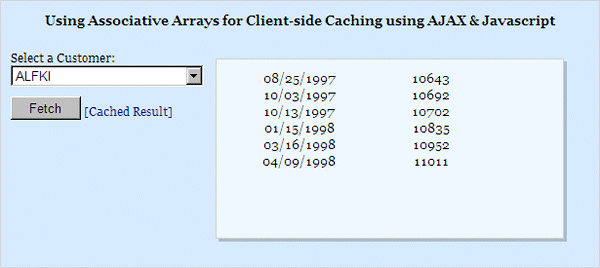
Add the needed JavaScript code now. We have a HTML button with the ID btnFetch. In the OnClick event, we trigger either an Ajax asynchronous call to the server or render from the cache.
function btnFetch_onclick()
{
currSel = document.getElementById("dlCustomers").value;
var status = document.getElementById("divStatus");
if(cacheData[currSel]==null)
{
DataAccess.FetchOrders(currSel,OnCompleteCallback,OnErrorCallback,
OnTimeOutCallback);
cacheData[currSel] = seedData;
status.innerHTML = "[Live Result]";
}
else
{
status.innerHTML = "[Cached Result]";
var cacheobject = FetchDataFromCache(currSel);
RenderData(cacheobject);
}
document.getElementById("dlCustomers").focus();
}
 One point to take careful note of is that if you are using multiple cache arrays in your page, you will have to maintain multiple states for the item currently selected. In that case, you might have additional state variables like
One point to take careful note of is that if you are using multiple cache arrays in your page, you will have to maintain multiple states for the item currently selected. In that case, you might have additional state variables like currProductSel, currCustSel etc. Of course, you will have to have multiple cache arrays as well
Conclusion
If employed correctly, client-side caching can be a great tool to enhance the user experience and make the web application more responsive. If your application is so designed, you may also consider prefetching data through Ajax calls and plonking them into the cache. Prefetching requires minimal code overhead and can be an additional boost to performance if your application warrants it.
