
Introduction
Quite simple way of creating the MS Excel document through C# language.
Background
Minimum understanding of C# language buzz
Using the code
Create a new project, for simplicity, create a Windows application, go ahead and right click on References in the Solution Explorer, and select Add Reference� When the Add Reference window comes up, select the COM tab. This will list all Component names which are available on your machine. Since we are going to use MS Excel, you will scroll down until you find: Microsoft Excel 11.0 Object Library. You can even do the same thing PIAs. In the code I have used PIA.
I have created a very simple wrapper class for Excel object model . The code will be given below. This project also has the error provider functionality to make sure that user will enter values for all the fields.
Create button click event. Here we checking whether all fields are filled and then call the CreateFile() function in Excel wrapper class
private void btnCreate_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
ExcelAuto excel = new ExcelAuto();
ArrayList array = new ArrayList();
bool filled = true;
if ( ( txtName.Text).Trim().Length.Equals(0) )
{
errorProvider.SetError(txtName,"cannot be empty" );
filled = false;
}
if( ( txtAge.Text ).Trim().Length.Equals(0) )
{
errorProvider.SetError( txtAge,"cannot be empty" );
filled = false;
}
if( ( txtDesignation.Text ).Trim().Length.Equals(0) )
{
errorProvider.SetError( txtDesignation,"cannot be empty" );
filled = false;
}
if( ( txtPlace.Text ).Trim().Length.Equals(0) )
{
errorProvider.SetError( txtPlace,"cannot be empty" );
filled = false;
}
if( ( txtEmail.Text ).Trim().Length.Equals(0) )
{
errorProvider.SetError( txtEmail,"cannot be empty" );
filled = false;
}
if( ( txtCompany.Text ).Trim().Length.Equals(0) )
{
errorProvider.SetError( txtCompany,"cannot be empty" );
filled = false;
}
if ( filled == true )
{
array.Insert(0,txtName.Text);
array.Insert(1,txtAge.Text);
array.Insert(2,txtDesignation.Text);
array.Insert(3,txtCompany.Text);
array.Insert(4,txtPlace.Text);
array.Insert(5,txtEmail.Text);
excel.CreateFile(array);
}
}
Excel File creation Code
public void CreateFile(ArrayList array)
{
object missing = System.Reflection.Missing.Value;
object fileName = "normal.dot";
object newTemplate = false;
object docType = 0;
object isVisible = true;
ExcelApp = new Excel.ApplicationClass();
ExcelApp.Visible = true;
objBook = ExcelApp.Workbooks.Add(missing);
objSheet = (Excel.Worksheet)objBook.Sheets["Sheet1"];
objSheet.Name = "It's Me";
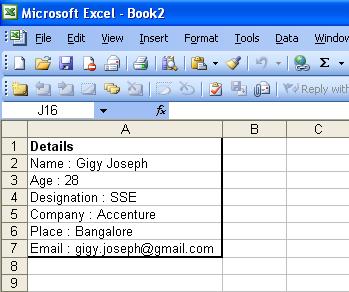
objSheet.Cells[1, 1] = "Details";
objSheet.Cells[2, 1] = "Name : "+ array[0].ToString();
objSheet.Cells[3, 1] = "Age : "+ array[1].ToString();
objSheet.Cells[4, 1] = "Designation : " + array[2].ToString();
objSheet.Cells[5, 1] = "Company : " + array[3].ToString();
objSheet.Cells[6, 1] = "Place : " + array[4].ToString();
objSheet.Cells[7, 1] = "Email : "+array[5].ToString();
objSheet.get_Range("A1", "A1").Font.Bold = true;
objSheet.get_Range("A1", "A6").EntireColumn.AutoFit();
objSheet.get_Range("A1","A7").BorderAround(Excel.XlLineStyle.xlContinuous,
Excel.XlBorderWeight.xlMedium,Excel.XlColorIndex.xlColorIndexAutomatic,
Excel.XlColorIndex.xlColorIndexAutomatic);
}
Conclusion
The interop assemblies provide a lot of options for working with Excel data, both reading and writing. I hope this article gives you a head start in controlling Excel from .NET and C#. Some experiment with the object model will help you to get that hands on
History
First draft 29 December 2006
