Introduction
Sooner or later, you will have an array of objects you'd like to sort. Unlike simple types like strings or integers, your objects usually have several properties you or your user want to sort on.
This article explains how to write a simple class which works with Array.Sort() to sort arrays of objects on dinamically selected fields. It's very similar to what DataView.Sort does for DataTables.
Background
Back in the old C times, when you wanted to use the standard sort or search functions you had to write a function to compare two objects of the desired type. The function received pointers to the objects, and returned -1, 0 or 1 when the first value was smaller, equal or bigger than the second.
You will then pass your function to the C sort function, using a function pointer (something similar to .NET's delegates).
This dirty but efficient technique allowed to create a single array sort function, that worked with any type of objects you wrote a comparer for.
Thinking in objects
In .NET, the approach to this problem is very similar. The Array.Sort method uses an IComparer with a method called Compare, that receives two objects and returns exactly the same as our old C comparer.
The class
The criteria to sort an array of objects is usually formed by the name of the fields, and an indication of ascending or descending order (like an SQL "ORDER BY" clause).
So, the constructor of our class accepts exactly those parameters:
public ObjectComparer(string[] fields, bool[] descending)
{
Fields = fields;
Descending = descending;
}
To make it easier to use, I also implemented a constructor for "all ascending" fields:
public ObjectComparer(params string[] fields) : this(fields, new bool[fields.Length]) {}
The alternate constructor just calls the first one with an array of false booleans for the descending parameter. Remember that, since bools are structs, they are initialized to 0 (false) on array creation.
Now, the method that does all the work
public int Compare(object x, object y)
{
Type typex = x.GetType();
Type typey = y.GetType();
for(int i = 0; i<Fields.Length; i++)
{
PropertyInfo pix = typex.GetProperty(Fields[i]);
PropertyInfo piy = typey.GetProperty(Fields[i]);
IComparable pvalx = (IComparable)pix.GetValue(x, null);
object pvaly = piy.GetValue(y, null);
int iResult = pvalx.CompareTo(pvaly);
if (iResult != 0)
{
if (Descending[i])
{
return -iResult;
}
else
{
return iResult;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
Note that I don't implement ANY error-checking code. It's such a simple class that it's not worth it. Be sure to call it with correct parameters (existing properties, and two same-size parameter arrays).
Comparing apples and bananas?
The key here, is that the two objects don't have to be the same type, as long as they implement the same property, and the property is a type that implements IComparable. So, you could sort Controls based on their TabIndex, since it's an Int32.
Using the code
First build the ObjectComparer library, and then open the PersonSort project.
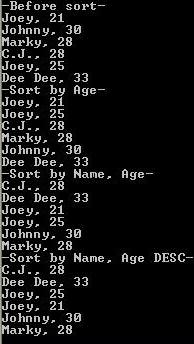
This sample project implements a simple class, Person, which represents a person with a Name (string) and an Age (int). We first create an array of persons:
Person[] personArray = new Person[]
{
new Person("Joey", 21),
new Person("Johnny", 30),
new Person("Marky", 28),
new Person("C.J.", 28),
new Person("Joey", 25),
new Person("Dee Dee", 33)
};
And then we can sort in any field we want:
Array.Sort(personArray, new ObjectComparer("Age"));
Array.Sort(personArray, new ObjectComparer("Name", "Age"));
Array.Sort(personArray, new ObjectComparer(
new string[]{"Name","Age"},
new bool[]{false,true}
));
Conclusion
ObjectComparer is a nice tool for sorting arrays of objects on programmer or user request.
Whenever you create this kind of utility class, it's important to create good constructors, so they can be created and used in just one line.
