Background
This is one of my favorite interview questions. This question helps me to find out if candidate has good knowledge of generics or not. On the internet, there are a number of writeups on "difference between Array and ArrayList" but I didn't find any on "difference between ArrayList and List", so I am posting one...
Must Know
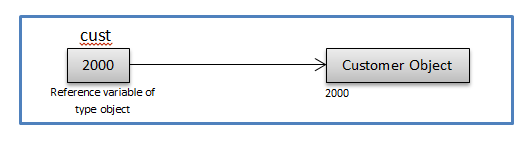
First, one should know what is upcasting? Upcasting is converting derived type into base type. In .NET, all data-types are derived from Object. So we can typecast any type to Object type. For example, if Customer is class, then we can create object of Customer like this:
Object cust = new Customer()
Here new Customer() will create object on heap and its address we are putting in reference variable of type Object.
ArrayList
ArrayList marks = new ArrayList();
marks.Add(50);
marks.Add(70.5);
marks.Add("Sixty");
In the above code snippet, we are creating object of ArrayList and adding different type of data in it. But actually ArrayList is a collection of Object type, and when we add any item to ArrayList, it first converts it to object type (upcasting) and then adds it to collection object.
Interesting Fact: As ArrayList can only create collection for Object type, it is said to be non-generic class. It might be confusing as it seems that we can add any datatype value like int, float, string to ArrayList collection so in that sense it should be called as generic class. But in fact, it internally converts all these datatypes in object type and then adds to collection.
We can visualise it as:

List
List<int> marks = new List<int>();
marks.Add(50);
marks.Add(70);
marks.Add(60);
In the above snippet, we can observe that while creating object of list class, we have mentioned datatype of collection we want to create. We need to pass datatype while creating object as List class doesn’t hard code it internally. So the above declaration will create marks as collection of integers; and not collection of objects as in case of ArrayList.
We can visualize it as:

Interesting fact: In the above collection “marks” you can only add integers and no other type. In that sense, it should be referred to as non-generic! But wait, using the same List class, you can also create collection of string type:
List<string> names = new List<string>();
Or even you can create collection of custom types. For example, collection of Student type can be created as:
List<Student> students = new List<Student>();
And as using same List class, now you are able to create collection of any data-type as integers, strings or students; this class is known as Generic class.
One of the benefits of using generic collection is no need of boxing and unboxing while tackling with collections of value types.
We can visualise List of string type (or any ref type) as:

