
Introduction
XML is definitely the best way to share data via the World Wide Web. I came across a situation where I needed to export the database table rows in XML file format. XML data can easily be integrated into web applications for many uses. However, at some point you want XML data added to a database and vice-versa.
ADO.NET Architecture

ADO.NET and the XML classes in the .NET Framework converge in the DataSet object. The DataSet can be populated with data from an XML source, whether it is a file or an XML stream. The DataSet can be written as World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) compliant XML, including its schema as XML Schema Definition language (XSD) schema, regardless of the source of the data in the DataSet.
The following table outlines the four core objects that make up a .NET data provider:
| Object | Description |
|---|
Connection | Establishes a connection to a specific data source. |
Command | Executes a command against a data source. Exposes parameters and can execute within the scope of a transaction from a Connection. |
DataReader | Reads a forward-only, read-only stream of data from a data source. |
DataAdapter | Populates a DataSet and resolves updates with the data source. |
I did this in ASP.NET with VB.NET code behind using "System.IO.StreamWriter". It is assumed that you have a SQL Server database running with tables in it.
Connection to Database
Start with the database connection here. I used SQL Server 2000 as my database. Write the following code in your web config file:
="1.0"="utf-8"
<configuration>
<appSettings>
<add key="ConnectionString"
value="data source=erp1;Initial Catalog=Inventory; UID=sa;pwd="/>
</appSettings>
<system.web>
Add the following line of code in your .aspx page:
Protected connect As SqlConnection = _
New SqlConnection(ConfigurationSettings.AppSettings("ConnectionString"))
Dim cmdXML As SqlCommand
Dim DScmdXML As SqlDataAdapter
Dim DSXML As New DataSet()
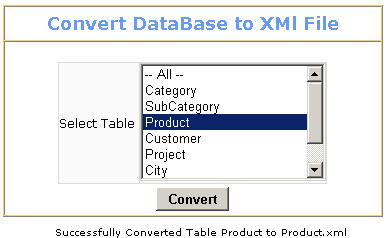
In this example, I have taken a ListBox which contains all the SQL Server database table names, manually adding the database table names as shown:
<asp:listbox id="ListBox1" runat="server"
Height="120px" Width="186px" SelectionMode="Multiple">
<asp:ListItem Value="1">Category</asp:ListItem>
<asp:ListItem Value="2">SubCategory</asp:ListItem>
<asp:ListItem Value="3">Product</asp:ListItem>
<asp:ListItem Value="8">City</asp:ListItem>
<asp:ListItem Value="9">State</asp:ListItem>
</asp:listbox>
To cut short the code I'm considering only the Product table. To test the program, select the "Product" table from the listbox and click the Convert button. The data of the Product table will be converted to Product.xml file. The program is simple and easy to understand. It's better programming to include the server side logic code in a Try … Catch block.
Main Logic
sqlXML = "Select ProductCode, ProductName from Product "
cmdXML = New SqlCommand(sqlXML, connect)
DScmdXML = New SqlDataAdapter(cmdXML)
DScmdXML.Fill(DSXML, "Product")
Response.Flush()
DSXML.WriteXml("Product.xml", XmlWriteMode.WriteSchema)
Dim xmlSW2 As System.IO.StreamWriter = New System.IO.StreamWriter("Product.xml")
DSXML.WriteXml(xmlSW2, XmlWriteMode.WriteSchema)
xmlSW2.Flush()
xmlSW2.Close()
How it works?
- Trap the user selected tables from the listbox using a '
For' loop and split array.
Select Case statement directs to suitable file creation.
- Open the database connection and open a
DataSet as shown in the example.
- Actual work is done by passing the file name for the resulting XML as a string to
WriteXml, and System.IO.StreamWriter writes to the XML file.
- Number of .xml files created depends on the number of tables selected from the listbox.
With a little trick you can create the XML file in any folder or subfolder and also the reverse is possible: i.e., a .xml file to a DataSet.
Important: Before converting to a .XML file, check the security settings of the folder where the file is saved.
