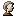
Introduction
I've been a member of the CodeProject for over 3 years now, and
still haven't contributed any articles - until now.
While designing a Windows Forms-based application, to administrate containers in
our Active Directory, I needed a way to allow binding to the AD using alternate
credentials. Windows impersonation was the answer. This sample app demonstrates
how to use unmanaged code by calling LogonUser() contained within the
advapi32.dll, and pass a token handle back to your .NET application using WindowsImpersonationContext.
One of the downfalls to the LogonUser()function is that the password get
passed in clear-text.
Partial Source Code
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Security.Principal;
using System.Security.Permissions;
...
public WindowsImpersonationContext
ImpersonateUser(string sUsername, string sDomain, string sPassword)
{
IntPtr pExistingTokenHandle = new IntPtr(0);
IntPtr pDuplicateTokenHandle = new IntPtr(0);
pExistingTokenHandle = IntPtr.Zero;
pDuplicateTokenHandle = IntPtr.Zero;
if (sDomain == "")
sDomain = System.Environment.MachineName;
try
{
string sResult = null;
const int LOGON32_PROVIDER_DEFAULT = 0;
const int LOGON32_LOGON_INTERACTIVE = 2;
bool bImpersonated = LogonUser(sUsername, sDomain, sPassword,
LOGON32_LOGON_INTERACTIVE, LOGON32_PROVIDER_DEFAULT,
ref pExistingTokenHandle);
if (false == bImpersonated)
{
int nErrorCode = Marshal.GetLastWin32Error();
sResult = "LogonUser() failed with error code: " +
nErrorCode + "\r\n";
MessageBox.Show(this, sResult, "Error",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
sResult += "Before impersonation: " +
WindowsIdentity.GetCurrent().Name + "\r\n";
bool bRetVal = DuplicateToken(pExistingTokenHandle,
(int)SECURITY_IMPERSONATION_LEVEL.SecurityImpersonation,
ref pDuplicateTokenHandle);
if (false == bRetVal)
{
int nErrorCode = Marshal.GetLastWin32Error();
CloseHandle(pExistingTokenHandle);
sResult += "DuplicateToken() failed with error code: "
+ nErrorCode + "\r\n";
MessageBox.Show(this, sResult, "Error",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
return null;
}
else
{
WindowsIdentity newId = new WindowsIdentity
(pDuplicateTokenHandle);
WindowsImpersonationContext impersonatedUser =
newId.Impersonate();
sResult += "After impersonation: " +
WindowsIdentity.GetCurrent().Name + "\r\n";
MessageBox.Show(this, sResult, "Success",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
return impersonatedUser;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ex;
}
finally
{
if (pExistingTokenHandle != IntPtr.Zero)
CloseHandle(pExistingTokenHandle);
if (pDuplicateTokenHandle != IntPtr.Zero)
CloseHandle(pDuplicateTokenHandle);
}
}
Points of Interest
This code won't work on Windows 98 or ME because they do not utilize user tokens. Code
was built and run using Visual Studio.NET 2002 on Windows XP Service Pack 1.
One of the other uses for this code I've found is, for instantiating COM components
that must run in an alternate security context to that of the logged-on user.
If anyone has a more secure method of achieving the same thing, please let me know.
History
- Version 1.0 - 04.25.03 - First release version
Living abroad and loving life.
 General
General  News
News  Suggestion
Suggestion  Question
Question  Bug
Bug  Answer
Answer  Joke
Joke  Praise
Praise  Rant
Rant  Admin
Admin