Sending Files using TCP
4.43/5 (23 votes)
Sending files using TCP
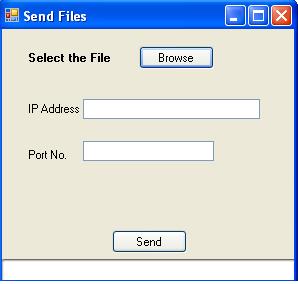
Introduction
A socket is an abstraction through which an application may send and receive data, in pretty much the same way as opening a file to read and write data. Different types of sockets correspond to different protocols. I will give you a brief description of TCP/IP protocol which has the main types of stream sockets and datagram sockets. Stream sockets use TCP and datagram sockets use UDP.
The .NET Framework has two classes for TCP which are TCPClient and TCPListener. A TCPClient initiates the communication with a server which is waiting for the connection. TCP is connection oriented and UDP is connectionless, which means that UDP sockets do not need to be connected before being used. Another difference between TCP and UDP is that there is no guarantee that a message sent via a UDP socket will arrive at its destination, and messages can be delivered in a different order than they were sent.
You have to carefully choose when you want to use TCP and when UDP. When you are sending a small amount of data, using TCP might double number of messages being sent and UDP provides minimal overhead platform.
Here I am going to show you a server/client application, by which you can send files using TCP.
Using the Code
Let’s talk about the client application first. The client application consists of an OpenFileDialog for selecting the file you want to send, two text boxes to enter server IP address and server port number, a label which show you the status of your application such as connected to the server or number of bytes that have been sent, a progress bar, and a button named send which sends data to the server.
When you are connected via TCP you create a network stream which you can read and write in, similar to all other streams you worked with. Writing a large amount of data to the stream is not a good idea, so I break the selected file into smaller packets in which each packet length is 1024 bytes (1KB) and then send all the packets to the server. The SendTCP function is as follows:
public void SendTCP(string M, string IPA, Int32 PortN)
{
byte[] SendingBuffer = null
TcpClient client = null;
lblStatus.Text = "";
NetworkStream netstream = null;
try
{
client = new TcpClient(IPA, PortN);
lblStatus.Text = "Connected to the Server...\n";
netstream = client.GetStream();
FileStream Fs = new FileStream(M, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
int NoOfPackets = Convert.ToInt32
(Math.Ceiling(Convert.ToDouble(Fs.Length) / Convert.ToDouble(BufferSize)));
progressBar1.Maximum = NoOfPackets;
int TotalLength = (int)Fs.Length, CurrentPacketLength, counter = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < NoOfPackets; i++)
{
if (TotalLength > BufferSize)
{
CurrentPacketLength = BufferSize;
TotalLength = TotalLength - CurrentPacketLength;
}
else
CurrentPacketLength = TotalLength;
SendingBuffer = new byte[CurrentPacketLength];
Fs.Read(SendingBuffer, 0, CurrentPacketLength);
netstream.Write(SendingBuffer, 0, (int)SendingBuffer.Length);
if (progressBar1.Value >= progressBar1.Maximum)
progressBar1.Value = progressBar1.Minimum;
progressBar1.PerformStep();
}
lblStatus.Text=lblStatus.Text+"Sent "+Fs.Length.ToString()+"
bytes to the server";
Fs.Close();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
finally
{
netstream.Close();
client.Close();
}
}
As you can see, a TCP client and a network stream are being constructed and a network connection is initiated. After opening the selected file according to the buffer size which is 1024 bytes, the number of packets that are going to be sent is calculated. There are two other variables CurrentPacketLength and TotalLength. If the total length of the selected file is more than the buffer size the CurrentPacketLength is set to the buffer size, otherwise why send some empty bytes, so CurrentPacketLength is set to the total length of the file. After that, I subtract the current from the total length, so actually we can say total length is showing the total amount of data that has not been sent yet. The rest is pretty much straight forward, reading the data from the file stream and writing it to the SendingBuffer according to the CurrentPacketLength and writing the buffer to the network stream. After all packets have been sent, the status will show the amount of bytes you have sent to the server.
At the server side, the application is listening for an incoming connection:
public void ReceiveTCP(int portN)
{
TcpListener Listener = null;
try
{
Listener = new TcpListener(IPAddress.Any, portN);
Listener.Start();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
byte[] RecData = new byte[BufferSize];
int RecBytes;
for (; ; )
{
TcpClient client = null;
NetworkStream netstream = null;
Status = string.Empty;
try
{
string message = "Accept the Incoming File ";
string caption = "Incoming Connection";
MessageBoxButtons buttons = MessageBoxButtons.YesNo;
DialogResult result;
if (Listener.Pending())
{
client = Listener.AcceptTcpClient();
netstream = client.GetStream();
Status = "Connected to a client\n";
result = MessageBox.Show(message, caption, buttons);
if (result == System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult.Yes)
{
string SaveFileName=string.Empty;
SaveFileDialog DialogSave = new SaveFileDialog();
DialogSave.Filter = "All files (*.*)|*.*";
DialogSave.RestoreDirectory = true;
DialogSave.Title = "Where do you want to save the file?";
DialogSave.InitialDirectory = @"C:/";
if (DialogSave.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
SaveFileName = DialogSave.FileName;
if (SaveFileName != string.Empty)
{
int totalrecbytes = 0;
FileStream Fs = new FileStream
(SaveFileName, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write);
while ((RecBytes = netstream.Read
(RecData, 0, RecData.Length)) > 0)
{
Fs.Write(RecData, 0, RecBytes);
totalrecbytes += RecBytes;
}
Fs.Close();
}
netstream.Close();
client.Close();
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
//netstream.Close();
}
}
}
A TCP listener is created and starts listening to the specified port. Again the buffer size is set to 1024 bytes. A TCP listener can pre check to see if there are any connections pending before calling the AcceptTcpClient method. It returns true if there are any pending connections. This method is a good way of avoiding the socket being blocked. Before reading anything from the network stream, a message box asks you if you want to accept the incoming connection, then a SaveFileDialog will be opened, and when you enter the file name plus extension, a file stream will be constructed and you start reading from the network stream and writing to the file stream. Create a thread in your code and run the receiving method in the created thread. I have sent more than 100 MB files in a LAN with the application.
History
- 18th January, 2009: Initial post
