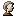[The VC6 version of source code is kept just for reference in case if any one is still using VC6. Also, it does not include any modifications done after June-06-2008 mentioned in the Revision History section.]
Introduction
This is a utility to display all the files that are opened under a specific folder.
Background
It often happens to me that when I try to rename or delete my current working folder of a project, it gives an error message like "Cannot rename BlaBlaBla: It is being used by another person or program". Almost at all times, I fail to find this other program/person, and end up restarting the machine. Since then, I have been searching for a method to find the list of files that an application uses. Even though the ProcessExplorer of SysInternals lists the files opened by each process, it is hard to find opened files in a particular folder. So I created one that does this, purely because of my necessity.
Using the Code
Download the application and register it using RegSvr32 (RegSvr32 OpenedFiles.dll). This application basically contains two components: an extension DLL and a driver. The extension DLL is responsible for showing the context menu in the shell and the GUI you see. I will explain the role of the driver later in this article.
This application will install a menu on folders, the background of a folder, and on a drive. I suggest you read The Complete Idiot's Guide to Writing Shell Extensions - Part I, article by Michael Dunn, if you are new to shell extensions. In fact, it was from there that I learned to write shell extensions.

Enumerating Opened Files
When you click on the "List Opened Files" menu, it will first enumerate all of the opened files in the system. This is implemented in the following function:
void EnumerateOpenedFiles( CString& csPath, OF_CALLBACL CallBackProc, UINT_PTR pUserContext,
HANDLE hDriver,
GetFinalPathNameByHandleDef pGetFinalPathNameByHandle )
{
...............
PSYSTEM_HANDLE_INFORMATION pSysHandleInformation = new SYSTEM_HANDLE_INFORMATION;
DWORD size = sizeof(SYSTEM_HANDLE_INFORMATION);
DWORD needed = 0;
NTSTATUS status = NtQuerySystemInformation( SystemHandleInformation,
pSysHandleInformation, size, &needed );
if( !NT_SUCCESS(status))
{
if( 0 == needed )
{
return; }
delete pSysHandleInformation;
size = needed + 1024;
pSysHandleInformation = (PSYSTEM_HANDLE_INFORMATION)new BYTE[size];
status = NtQuerySystemInformation( SystemHandleInformation,
pSysHandleInformation, size, &needed );
if( !NT_SUCCESS(status))
{
delete pSysHandleInformation;
return;
}
}
.....................
.....................
.....................
for ( DWORD i = 0; i < pSysHandleInformation->dwCount; i++ )
{
SYSTEM_HANDLE& sh = pSysHandleInformation->Handles[i];
if( sh.bObjectType != nFileType ) {
continue;
}
CString csFileName;
CString csDir;
if( hDriver )
{
HANDLE_INFO stHandle = {0};
ADDRESS_INFO stAddress;
stAddress.pAddress = sh.pAddress;
DWORD dwReturn = 0;
BOOL bSuccess = DeviceIoControl( hDriver, IOCTL_LISTDRV_BUFFERED_IO,
&stAddress, sizeof(ADDRESS_INFO),
&stHandle,
sizeof(HANDLE_INFO), &dwReturn, NULL );
if( bSuccess && stHandle.tcFileName[0] != 0 &&
stHandle.uType != FILE_DEVICE_SOUND &&
stHandle.uType != FILE_DEVICE_NAMED_PIPE )
{
if( stHandle.uType != FILE_DEVICE_NETWORK_FILE_SYSTEM )
{
if( !GetDrive( (LPCTSTR)stHandle.tcDeviceName, csFileName, true ))
{
OutputDebugString( L"GetDrive failed" );
}
csFileName += (LPCTSTR)stHandle.tcFileName;
}
else
{
csFileName = _T("\\");
csFileName += (LPCTSTR)stHandle.tcFileName;
}
}
}
...
For every file opened in the system, there will be a handle associated with it. With the NtQuerySystemInformation API, we can retrieve all the handles in the system. This includes file handles, Mutex handles, Event handles, etc. Actually, the NtQuerySystemInformation function returns an array of the structure SYSTEM_HANDLE.
typedef struct _SYSTEM_HANDLE
{
DWORD dwProcessId;
BYTE bObjectType;
BYTE bFlags;
WORD wValue;
PVOID pAddress;
DWORD GrantedAccess;
}
SYSTEM_HANDLE;
For an object of type file, the value bObjectType in SYSTEM_HANDLE is 28 in Windows XP, Windows 2000, and Window 7; 25 in Windows Vista; and 26 in Windows 2000. Since this application supports only XP/Windows 7, Windows 2000, and Vista, we can ignore all the items with values other than 28/25. In SYSTEM_HANDLE, there is another important member for us, the pAddress. For each file handle, there is a FILE_OBJECT associated with it, and the pAddress is a pointer to that structure. Unfortunately, this address points to kernel memory space, and a user mode application cannot access this memory. Here comes the driver part. This application accesses this memory using the driver "ListOpenedFileDrv_XX.sys". The only thing the driver does is copy the file name in the kernel memory and pass it to the user mode. Using the function DeviceIoControl, the pAddress is passed to the driver. The driver accepts this address and copies the file name from FILE_OBJECT, setting it in the out parameter of the DeviceIoControl function.
As I mentioned earlier, the Process Explorer shows the information about all the handles used by the application. However, the Process Explorer is a stand-alone application. So where is the driver? Or is it doing all this without the driver? This question puzzled me for many days until someone told me that the driver is added in the resource of the Process Explorer. Nice trick, isn't it? So I thought of implementing the same feature in my application too. The function given below performs this task. [Note: The new version of the application is not keeping the driver in the resource, but it directly uses the driver from the application folder. The below code is kept only for those who refer to the VC6 version of the source code.]
HANDLE ExtractAndInstallDrv()
{
SC_HANDLE hSCManager =
OpenSCManager( NULL, NULL, SC_MANAGER_ALL_ACCESS );
SC_HANDLE hService = OpenService
( hSCManager , DRV_NAME, SERVICE_ALL_ACCESS);
CString csPath;
if( 0 == hService )
{
HINSTANCE hModule= AfxGetInstanceHandle();
HRSRC hRsrc = FindResource
(hModule, MAKEINTRESOURCE(IDR_XPDRIVER),_T("BINARY"));
HGLOBAL hDrvRsrc = LoadResource(hModule, hRsrc);
DWORD dwDriverSize = SizeofResource(hModule, hRsrc);
LPVOID lpvDriver = LockResource(hDrvRsrc);
CFile File;
if( !File.Open( DRV_FILE_NAME, CFile::modeCreate|CFile::modeWrite ))
{
return 0;
}
File.Write( lpvDriver, dwDriverSize );
csPath = File.GetFilePath();
File.Close();
...
}
I made an application that does the above things and started using it. Some days later, again that rename problem occurred, and my application listed nothing. When I looked in the Task Manager, I found out that this time it was because of the applications that were running from my folder. So my next step was to enumerate the EXEs and any DLLs that have been loaded from my folder.
Enumerating Loaded Modules
Enumerating the modules loaded by applications was somewhat easy compared to the above task. It just made use of the following APIs. The EnumerateLoadedModules function handles this task in the application.
EnumProcesses()
CreateToolhelp32Snapshot()
Module32First()
Module32Next()
Compatibility with UAC
As you have seen, this application makes use of many API calls that need Administrative privilege. But the Explorer.exe in Vista and later runs with restricted privilege so that the shell extension loaded by the explorer also cannot make any API calls that need Administrative privilege. Which means my current implementation, which had only one DLL that does all the job, is no longer going to work. So the only way is to spool another EXE from the shell extension in Administrative mode. So now, when you click on "List Opened Files", it launches OpenFileFinder.exe using ShellExecute, and the rest of the things are taken care by this process. But I was so lazy to move all the existing feature of in the shell extension DLL to the exe or another DLL. So what I did is I kept the functionality in the DLL itself and exported the function ShowOpenedFiles from the DLL, which when called, shows the opened files dialog. The diagram below show this architecture:

The Problem with Vista 64 Bit and Windows-7 64 Bit
In 64 bit versions of Windows, starting from Vista, Microsoft has enforced that any program that is supposed to be loaded into the kernel space should be digitally signed by Microsoft. This enforcement affect lots of free software and unfortunately to this software also. The core thing in this application is done by our tiny driver which I no longer will be able to load in those versions of Windows. So my initial plan was to discontinue this application in 64 bit Vista and later. However, because of the new APIs which are introduced from Windows Vista, there is still an option to make this work without the driver also. So this application still works in 64 bit Vista and Windows with limited results. The new API that I was talking about is GetFinalPathNameByHandle. However, using the API instead of our driver has some problems like:
- This function accepts
HANDLE, but the handles are not unique among all processes. - To solve the above problem, we have to duplicate the handle. To duplicate the handle, I have to get the process handle using
OpenProcess. But OpenProcess fails for some processes like SYSTEM because of lack of access. Even if we successfully duplicate some other handles, the API still fails saying Access Denied. - Last and the worst, it hangs for certain kinds of handles. You can read mode about this problem in here: GetFinalPathNameByHandle API Hungs. At the time when I was checking this problem in Windows Vista, I remember atleast the
GetFileInformationByHandleEx worked in all cases. But now I experience the same problem in Windows 7.
The only workaround to prevent the entire application from hanging is to call the API from a separate thread. So what I did in this application is, if the driver installation fails, it will switch to Plan B, which is actually to use the GetFinalPathNameByHandle in a separate thread. Meanwhile, the main thread will keep on checking whether the worker thread has hung or not using some events. After a time out period, if the main thread does not receive the event, it will terminate the worked thread and spool another worker thread. This is continued until all the the handles have been enumerated.
The following code shows how the API is called from the thread:
DWORD WINAPI ThreadProc( LPVOID lParam )
{
THREAD_PARAMS* pThreadParam = (THREAD_PARAMS*)lParam;
GetFinalPathNameByHandleDef pGetFinalPathNameByHandle =
pThreadParam->pGetFinalPathNameByHandle;
for( g_CurrentIndex; g_CurrentIndex < pThreadParam->pSysHandleInformation->dwCount; )
{
WaitForSingleObject( pThreadParam->hStartEvent, INFINITE );
ResetEvent( pThreadParam->hStartEvent ).
pThreadParam->bStatus = false;
SYSTEM_HANDLE& sh = pThreadParam->pSysHandleInformation->Handles[g_CurrentIndex];
g_CurrentIndex++;
HANDLE hDup = (HANDLE)sh.wValue;
HANDLE hProcess = OpenProcess( PROCESS_DUP_HANDLE , FALSE, sh.dwProcessId );
if( hProcess )
{
BOOL b = DuplicateHandle( hProcess, (HANDLE)sh.wValue,
GetCurrentProcess(), &hDup, 0, FALSE, DUPLICATE_SAME_ACCESS );
if( !b )
{
hDup = (HANDLE)sh.wValue;
}
CloseHandle( hProcess );
}
DWORD dwRet = pGetFinalPathNameByHandle( hDup, pThreadParam->lpPath, MAX_PATH, 0 );
if( hDup && (hDup != (HANDLE)sh.wValue))
{
CloseHandle( hDup );
}
if(dwRet)
{
pThreadParam->bStatus = true;
}
SetEvent( pThreadParam->hFinishedEvent );
}
return 0;
}
And this is how the main thread delegates its work to the thread procedure:
void EnumerateOpenedFiles( CString& csPath, OF_CALLBACL CallBackProc,
UINT_PTR pUserContext, HANDLE hDriver,
GetFinalPathNameByHandleDef pGetFinalPathNameByHandle )
{
................
................
if( pGetFinalPathNameByHandle ) {
g_CurrentIndex = 0;
TCHAR tcFileName[MAX_PATH+1];
THREAD_PARAMS ThreadParams;
ThreadParams.lpPath = tcFileName;
ThreadParams.nFileType = nFileType;
ThreadParams.pGetFinalPathNameByHandle = pGetFinalPathNameByHandle;
ThreadParams.pSysHandleInformation = pSysHandleInformation;
ThreadParams.hStartEvent = ::CreateEvent( 0, TRUE, FALSE, 0 );
ThreadParams.hFinishedEvent = ::CreateEvent( 0, TRUE, FALSE, 0 );
HANDLE ThreadHandle = 0;
while( g_CurrentIndex < pSysHandleInformation->dwCount )
{
if( !ThreadHandle )
{
ThreadHandle = CreateThread( 0, 0, ThreadProc, &ThreadParams, 0, 0 );
}
ResetEvent( ThreadParams.hFinishedEvent );
SetEvent( ThreadParams.hStartEvent );
if( WAIT_TIMEOUT == WaitForSingleObject( ThreadParams.hFinishedEvent, 100 ))
{
CString csError;
csError.Format(L"Query hang for handle %d",
(int)pSysHandleInformation->Handles[g_CurrentIndex - 1].wValue);
OutputDebugString(csError );
TerminateThread( ThreadHandle, 0 );
CloseHandle( ThreadHandle );
ThreadHandle = 0;
continue;
}
if( !ThreadParams.bStatus )
{
continue;
}
................
................
}
Compared to the driver method, this one is much slower and returns less results. You have to switch off the diver signature enforcement in 64 bit Vista if you still want this application to work using the driver.
How Third Party Applications Can Make Use of This Application
After the initial version of this application, I received many requests from people to export some functions so that other applications can also make use of this functionality. Starting from this release, OpenFileFinder.dll exports two C functions, which can be called from other binaries:
void ShowOpenedFiles( LPCWSTR lpPath )You can call this function if you want to show the dialog and display the opened files in it.
void GetOpenedFiles( LPCWSTR lpPath, OF_TYPE Filter,OF_CALLBACK CallBackProc,UINT_PTR pUserContext );If you call this function and pass a callback pointer, for each file handle that matches the input path, the callback function will be called.
The above functions plus the OF_TYPE enum and the OF_CALLBACK function pointer is defined in OpenedFiles.h.
Close Handle Option
During the initial development of this utility, I purposefully ignored the option for closing any file handles opened by another process. I though it was unsafe if it provides such an option because closing the handle may lead to unexpected results in that application. However, I later got into some situations like the folder I wanted to rename was used by service.exe. And if I wanted to rename the folder, the only option was to terminate the process. But terminating service.exe will make the entire system unstable. And so I was forced to include a Close Handle option too.
So how this option basically works is, it duplicates the handle using the DuplicateHandle() function with the DUPLICATE_CLOSE_SOURCE flag specified. After that, it closes the duplicate handle also using the CloseHandle() function. This option will work only for loaded files; i.e., using this option on a DLL used by another process is just ignored.
HANDLE hDup = 0;
BOOL b = DuplicateHandle( hProcess, hFile, GetCurrentProcess(),
&hDup, DUPLICATE_SAME_ACCESS , FALSE, DUPLICATE_CLOSE_SOURCE );
if( hDup )
{
CloseHandle( hDup );
}
CloseHandle( hProcess );
Basically, with the above code, we can close the handles created by another process. After closing the handle, we can rename or delete that file or directory. But there are cases where after closing the handle, we can rename the folder but deleting is not possible. For example, consider the file C:\WINDOWS\system32\config\CstEvent.Evt. Normally, this file is used by Service.exe for event logging purposes. So if we try to close this file handle using the above option, the handle will be closed and we can rename too, but cannot delete!! I tried many ways to solve this, but couldn't come up with a working solution. If anybody knows any options to solve this, please let me know.
Miscellaneous Features
Auto Complete in Combobox

You have probably noticed that when we type some paths in the Run dialog of Windows, it will list the files and folders under that path. Similarly, when you type a path in the combobox of this application, it will list the files and folders under that path. SHAutoComplete takes care of this feature. This function needs a handle of the edit control. But I only have a combobox - how do I take the edit control inside it? Well, the edit control inside the combobox has a control ID 1001. Use the GetDlgItem() function with this ID to get the handle of the edit control. You can also specify a filename in that combobox.
BOOL MainDlg::OnInitDialog()
{
.....
CWnd* pEdit = m_combobox.GetDlgItem( 1001 );
if( pEdit )
{
SHAutoComplete( pEdit->m_hWnd, SHACF_FILESYSTEM );
}
}
Find Target Option
When you right click on one item in the list control of this application, you will find a menu called "Find Target". This option is something like the Find Target option in Windows Explorer. It opens a Windows Explorer window with a specified file selected in its folder. SHOpenFolderAndSelectItems() is used for implementing this feature.
void MainDlg::OnMainFindtarget()
{
....
CString csPath;
csPath = m_list.GetItemText( nItem,2 );
LPITEMIDLIST stId = 0;
SFGAOF stSFGAOFIn = 0;
SFGAOF stSFGAOFOut = 0;
if( !FAILED(SHParseDisplayName( csPath, 0, &stId,stSFGAOFIn, &stSFGAOFOut )))
{
SHOpenFolderAndSelectItems( stId, 0, 0, 0 );
}
}
Show Loaded Modules and Show Loaded Files - Options
As mentioned above, the list control in the application list includes two types of items - loaded files and loaded modules (DLLs, OCX, EXE etc.). This option is to Show/Hide one type of item from the list.
Note
This application uses a driver built for Windows XP/Win2003/Vista/Window 7, and so it will run only on those versions. If you want, you can add support for other OS versions as well by building the driver and making the necessary changes to the application.
Revision History
September-29-2010
- Added 64 bit support
- Added modifications mentioned in the section "Compatibility with UAC"
- Added modifications mentioned in the section "The problem with Vista 64 bit and Windows-7 64 bit"
June-06-2008
- The bug described in the below post[^] has been fixed
- Close Handle and Close All Handle options added
- "Show Loaded Modules" and "Show Loaded Files" options added
October-12-2007
- Application icon is displayed along with process
- Miscellaneous Features section added
September-27-2007
- "Find Target" menu added
- Added driver for Windows Vista
- Added VC8 solution
June-30-2007
June-4-2007
May-28-2007
This member has not yet provided a Biography. Assume it's interesting and varied, and probably something to do with programming.
 General
General  News
News  Suggestion
Suggestion  Question
Question  Bug
Bug  Answer
Answer  Joke
Joke  Praise
Praise  Rant
Rant  Admin
Admin